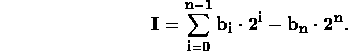
Positive two's complement integers have the same representation as unsigned numbers.
The additive inverse in two's complement is formed by taking the one's complement of a number and then adding 1 to the least significant bit.
Comparing this procedure to one's complement, it is easy to see that the value of an (n+1) bit two's complement integer is:
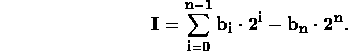
The range of values for an (n+1) bit two's complement integer is
![]() to
to ![]() .
.
Since the additive inverse of 0 is 0 in two's complement, the zero value has a unique representation.
To find the 8 bit two's complement representation of -8:
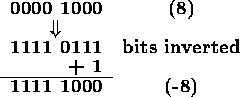
Examples of 8-bit two's complement numbers:
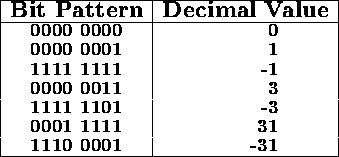
The range of 8-bit two's complement integers is -128 to +127.
Addition of signed numbers in two's complement is performed using simple binary addition.
To add decimal 17 to decimal -8 in 8-bit two's complement:
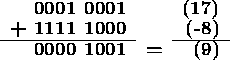
A carry out of the most significant bit is ignored in two's complement addition.