


Next: Compiler Phases
Up: Compiler Overview
Previous: Compiler Compilers
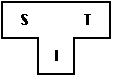
A compiler is characterized by three languages:
- Source Language
- Target Language
- Implementation Language
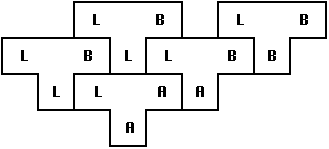
Notation: 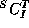 represents a compiler for Source S, Target T,
implemented in I. The T-diagram shown above is also used to
depict the same compiler.
represents a compiler for Source S, Target T,
implemented in I. The T-diagram shown above is also used to
depict the same compiler.
To create a new language, L, for machine A:
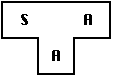
- Create
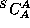 , a compiler for a subset, S, of the desired
language, L, using language A, which runs on machine A.
(Language A may be assembly language.)
, a compiler for a subset, S, of the desired
language, L, using language A, which runs on machine A.
(Language A may be assembly language.)
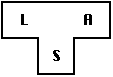
- Create
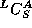 , a compiler for language L written in a subset
of L.
, a compiler for language L written in a subset
of L. - Compile
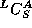 using
using 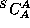 to
obtain
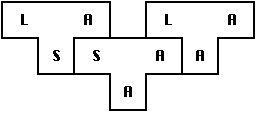
to
obtain 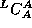 , a compiler for language L, which runs on machine
A and produces code for machine A.
, a compiler for language L, which runs on machine
A and produces code for machine A.

The process illustrated by the T-diagrams is called bootstrapping and
can be summarized by the equation:

To produce a compiler for a different machine B:
- Convert
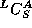 into
into 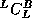 (by hand, if necessary).
Recall that language S is a subset of language L.
(by hand, if necessary).
Recall that language S is a subset of language L. - Compile
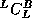 to produce
to produce 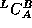 , a cross-compiler
for L which runs on machine A and produces code for machine B.
, a cross-compiler
for L which runs on machine A and produces code for machine B. - Compile
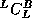 with the cross-compiler to produce
with the cross-compiler to produce
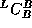 , a compiler for language L which runs on machine B.
, a compiler for language L which runs on machine B.
CS 631 Class Account
Thu Sep 14 11:55:16 ADT 2000

![]() represents a compiler for Source S, Target T,
implemented in I. The T-diagram shown above is also used to
depict the same compiler.
represents a compiler for Source S, Target T,
implemented in I. The T-diagram shown above is also used to
depict the same compiler.


![]()

![]()
