


Next: Example: Character to Numeric
Up: Data Representation
Previous: Sign Extension
Non-numerical data includes:
- letters: a-z and A-Z
- digits: 0-9
- symbols: ! # $ + - * / = _ ( ) [ ] etc.
- control characters: <CR> <LF> <BEL> <BS> etc.
Up to 256 characters may be encoded using 1 byte.
The American Standard for Computer Information Interchange (ASCII)
contains 128 characters.
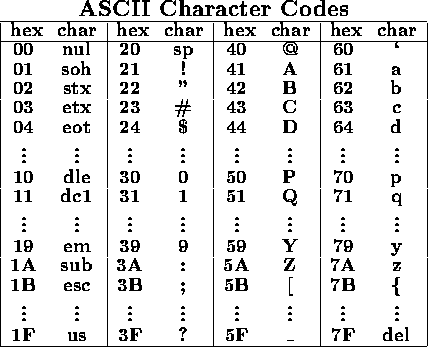
Notes:
ASCII codes for digits are not equal to the numeric values of the digits.
For example, ASCII 3 is 0x33.
When character codes are interpreted as unsigned integers:
- Character codes for digits are in numeric order.
- The rightmost hex digit of a digit code equals the numeric value of
the digit.
- Character codes for letters are in alphabetic order.
- Uppercase and lowercase alphabetic codes differ by 0x20.
(Shift key clears bit
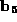 .)
.) - Control (nonprinting) characters differ from lowercase alphabetic
characters by 0x60. (Ctrl key clears bits
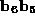 .)
.)
CS 301 Class Account
Mon Sep 14 23:38:35 ADT 1998

