The unsigned representation for the bias value, B, becomes the 0 value in biased representation.
Bias values begin at -B and increase in the direction of the 0 value.
The integer represented by an (n+1) bit biased-B representation is:
![]()
The range of values for an (n+1) bit biased-B representation is from -B to
![]()
The bias value, B, is usually ![]() or
or ![]() for an (n+1) bit
representation, which gives a range of values from approximately
for an (n+1) bit
representation, which gives a range of values from approximately
![]() to
to ![]() .
.
For example, a three bit biased representation with B = ![]() = 4 is:
= 4 is:
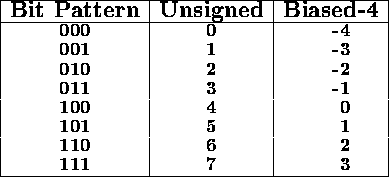
For an 8 bit biased representation, the bias would be either 127 or 128 and the range of values would be approximately -128 to +128.
When the bias equals ![]() or
or ![]() , the leftmost bit
indicates the sign of the number, but is inverted from the sign-magnitude
and complement representations.
, the leftmost bit
indicates the sign of the number, but is inverted from the sign-magnitude
and complement representations.
Negative bias values precede the 0 value with leftmost bit = 0, while positive bias values follow the 0 value with the leftmost bit = 1.