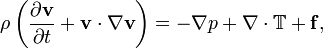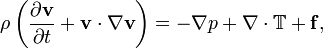| Symbol |
Pronounced |
Mathematical Definition |
Input Output |
Meaning |
| ∇A |
"gradient A" "grad A" or "del A" |
vec3(∂A / ∂x, ∂A / ∂y, ∂A / ∂z) |
scalar vector |
The gradient vector points
in the direction of greatest change. |
| ∇ . A | "divergence A" or "div A" |
∂A.x / ∂x + ∂A.y / ∂y + ∂A.z / ∂z |
vector scalar |
Positive divergence indicates areas
where a vector field is leaving. Negative indicates convergence, where field is arriving. |
| ∇ . ∇ A or ∇2A or ∆A | "laplace A" or "div grad A" |
∂2A / ∂x2 + ∂2A / ∂y2 + ∂2A / ∂z2 |
scalar scalar |
The Laplace
operator shows
up in diffusion, and other energy minimization problems. |
| ∇ x A | "curl A" "vorticity A" or "rot A" |
vec3(∂A.z / ∂y - ∂A.y / ∂z, ∂A.x / ∂z - ∂A.z / ∂x, ∂A.y / ∂x - ∂A.x / ∂y) |
vector vector |
The curl operator
measures local rotation. The magnitude of the curl indicates rotational speed. The direction of the curl indicates the rotational axis. |